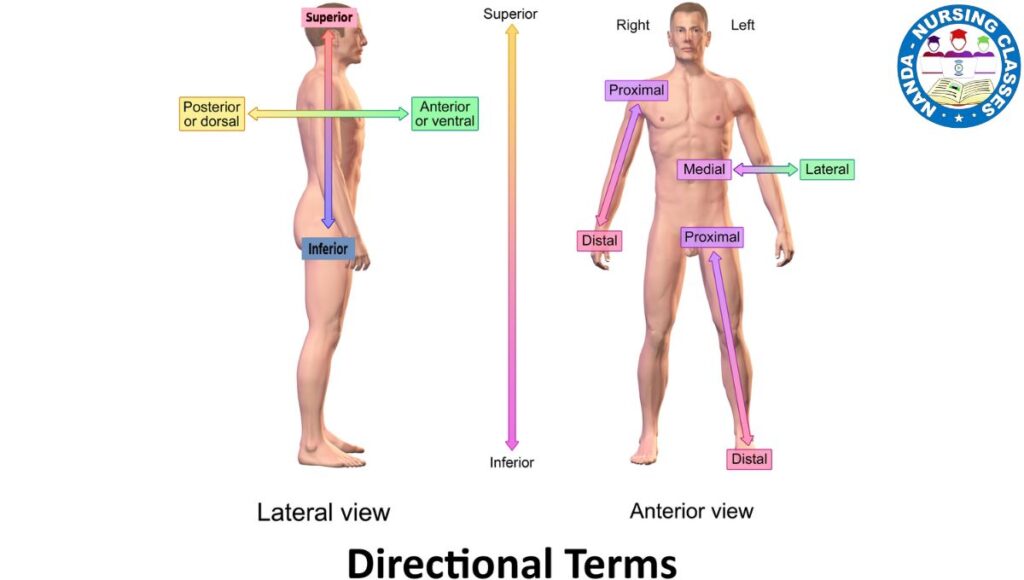
The human body Cavities and Organ Systems is intricate and well-organized systems made up of various structures working together to sustain life. At its core, this system relies on organ systems—groups of organs that perform specific, interconnected functions—to maintain health and equilibrium. These organ systems are strategically housed within body cavities, which provide protection, support, and space for their efficient functioning. Divided into two primary categories, dorsal and ventral, these cavities not only safeguard vital organs but also allow for specialized roles essential to survival. Exploring the relationship between organ systems and their respective cavities offers valuable insights into how the human body operates as a cohesive unit. This foundational knowledge is especially critical for fields like medicine, nursing, and allied health sciences. Let’s overview Human Body Cavities and Organ Systems.
Human Body Cavities and Organ Systems
Content in this page
Hunan body Major Systems:
-
- Skeletal System: Supports the body and protects organs.
- Muscular System: Enables movement and maintains posture.
- Circulatory System: Transports blood, nutrients, and oxygen.
- Respiratory System: Facilitates breathing and gas exchange.
- Digestive System: Breaks down food for energy.
- Nervous System: Processes information and controls responses.
- Endocrine System: Regulates hormones and body functions.
- Immune System: Protects against infections.
- Urinary System: Removes waste and regulates fluids.
- Reproductive System: Enables reproduction.
These are all systems we will learn about in an upcoming post so keep connected with us.
Human Body Cavities and Their Contents
The human body has several cavities or spaces that house and protect vital organs. These cavities are divided into two main categories: ventral body cavity & dorsal body cavity. Below is a detailed breakdown of these cavities, their contents, and their significance:
Ventral Body Cavity
The ventral body cavity is located on the front (anterior) side of the body. It is divided into Thoracic, abdominal and pelvic cavity.
Thoracic Cavity
- Location: Chest area, above the diaphragm.
- Contents:
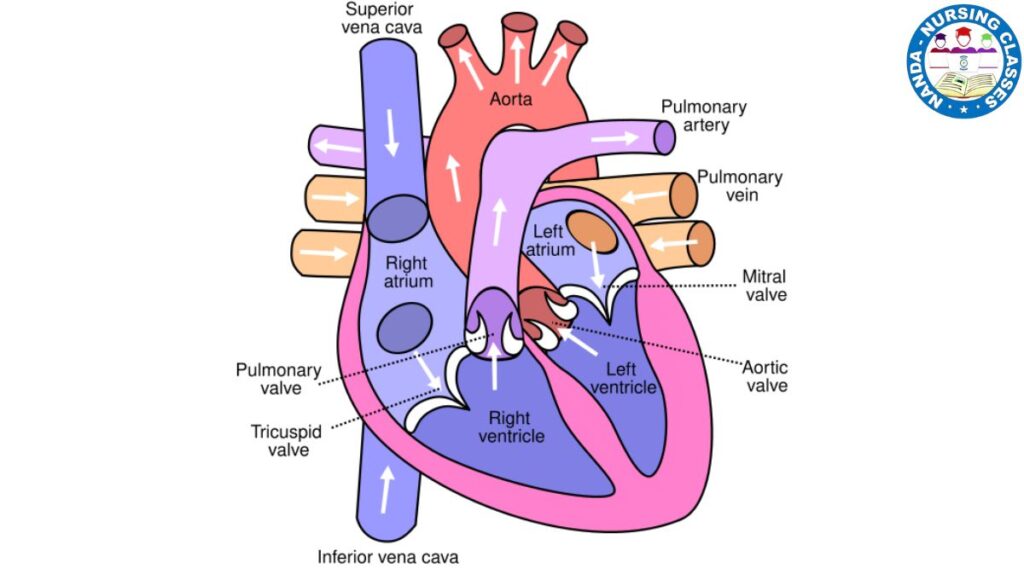
- Lungs: Facilitate breathing and gas exchange.
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body.
- Esophagus: Connects throat to stomach for food transport.
- Trachea: Carries air to the lungs.
- Significance: Surrounded by the rib cage to protect vital organs.
Abdominopelvic Cavity
The abdominopelvic cavity is divided into two regions abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
Abdominal Cavity:
-
-
- Contents:
- Stomach: Digests food.
- Liver: Processes nutrients and detoxifies.
- Pancreas: Produces enzymes and insulin.
- Small and Large Intestines: Absorb nutrients and water.
- Spleen: Filters blood and supports immunity.
- Significance: Protected by the abdominal muscles and fat layers.
- Contents:
-
Pelvic Cavity:
-
-
- Contents:
- Urinary Bladder: Stores urine.
- Reproductive Organs: Includes ovaries, uterus, testes, etc.
- Rectum: Excretes waste.
- Significance: Enclosed by the pelvis bones for support and protection.
- Contents:
-
Dorsal Body Cavity
The dorsal body cavity is located along the back (posterior) side of the body. It is divided into two sub-cavities Cranial Cavity and Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity
Cranial Cavity
- Location: Inside the skull (cranium).
- Contents:
- Brain: Controls bodily functions and processes information.
- Pituitary gland: Regulates hormones and body functions.
- Significance: Protects the brain with the bony skull and cerebrospinal fluid.
Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity
- Location: Within the vertebral column (spinal cord region).
- Contents:
- Spinal Cord: Transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
- Significance: Encased by vertebrae to provide protection and support.
Smaller Cavities
In addition to the main cavities, there are smaller cavities in the body:
- Oral Cavity (Mouth): Contains teeth and tongue.
- Nasal Cavity: Filters and moistens air for respiration.
- Orbital Cavities: House the eyes.
- Middle Ear Cavities: Contain structures for hearing.
Importance of Body Cavities
- Protection: Encases organs to shield them from injury.
- Support: Provides structural stability.
- Functionality: Allows for organ movement and expansion (e.g., lungs while breathing).
- Division of Tasks: Separates functions, preventing interference between organ systems.
Summary of Organ Systems in Body Cavities
- Nervous System: Brain and spinal cord (dorsal cavity).
- Respiratory System: Lungs and trachea (thoracic cavity).
- Cardiovascular System: Heart and blood vessels (thoracic cavity).
- Digestive System: Stomach, intestines, liver, etc. (abdominopelvic cavity).
- Reproductive System: Ovaries, uterus, testes (pelvic cavity).
- Urinary System: Kidneys, bladder (abdominopelvic cavity).
By understanding body cavities and their contents, nursing students can better comprehend how organ systems are organized and work collaboratively to maintain homeostasis. They can also appreciate how the body’s structure supports its functions.
Summary of Human Body Cavities and Their Contents
The human body has spaces called body cavities that house, protect, and support internal organs. These cavities are categorized into two main groups:
- Dorsal Body Cavity: Located at the back (posterior) side of the body.
- Cranial Cavity: Protects the brain and the pituitary gland.
- Spinal Cavity: Houses the spinal cord, enclosed by the vertebrae.
- Ventral Body Cavity: Found at the front (anterior) side of the body.
- Thoracic Cavity: Contains the lungs, heart, trachea, and esophagus, protected by the rib cage.
- Abdominopelvic Cavity: Subdivided into:
- Abdominal Cavity: Houses the stomach, liver, intestines, pancreas, and spleen.
- Pelvic Cavity: Contains the urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum.
Additionally, smaller cavities like the oral cavity, nasal cavity, orbital cavities (eyes), and middle ear cavities serve specific functions.
These cavities provide structural support, protect vital organs, and allow efficient organ functioning within their respective organ systems. Understanding body cavities is essential for grasping how the body is organized and how its systems interact to maintain health and homeostasis.
let’s see Anatomy and Physiology Other Topics
FAQs on Human Body Cavities and Their Contents
What are body cavities?
Body cavities are spaces within the body that enclose, protect, and support internal organs, allowing them to function effectively.
What are the two major body cavities?
The two main categories are:
- Dorsal body cavity (posterior), which includes the cranial and spinal cavities.
- Ventral body cavity (anterior), which includes the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
What is housed in the cranial cavity?
The cranial cavity contains the brain and the pituitary gland, essential for regulating bodily functions and processing information.
What is the function of the thoracic cavity?
The thoracic cavity protects and supports vital organs like the heart and lungs. It also houses structures such as the trachea and esophagus.
What is the difference between the abdominal and pelvic cavities?
- Abdominal cavity: Contains digestive organs like the stomach, intestines, and liver.
- Pelvic cavity: Contains reproductive organs, the bladder, and the rectum.
How do body cavities protect organs?
Body cavities provide physical barriers (e.g., the rib cage for the heart and lungs) and cushioning (e.g., cerebrospinal fluid for the brain and spinal cord) to safeguard organs from injury.
Why are smaller cavities like the orbital or nasal cavity important?
These smaller cavities support specialized functions, such as vision (orbital cavity) and respiration (nasal cavity).
How are body cavities connected to organ systems?
Each body cavity houses specific organs that belong to one or more organ systems. For example:
- The thoracic cavity contains organs of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
- The abdominopelvic cavity contains organs of the digestive, reproductive, and urinary systems.
It’s the last part of our continuing learning unit in that we learn about Body cavities and their contents in the human body. In the Third Part.
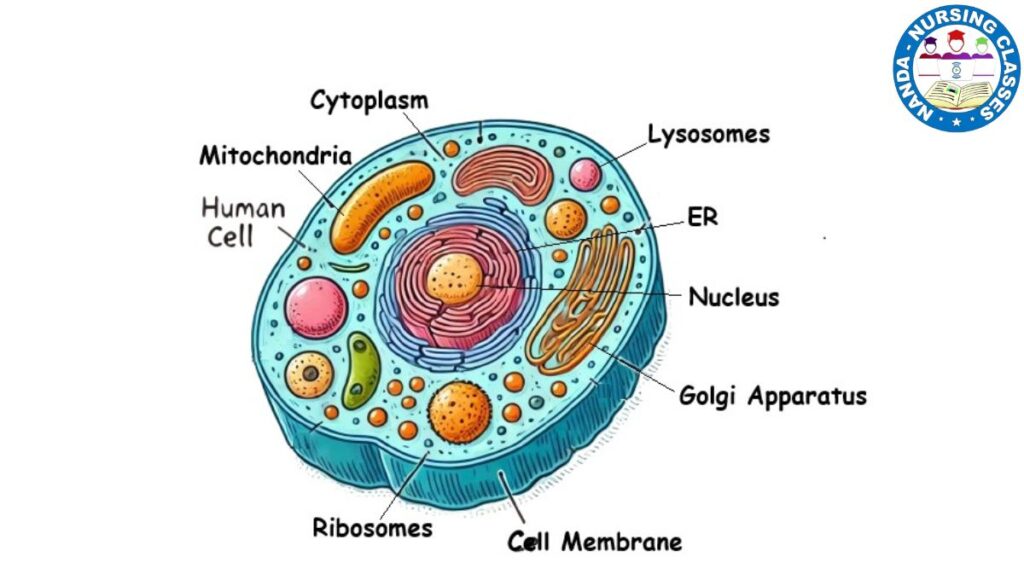
learn all about The Cells of the human body. In the First Part,
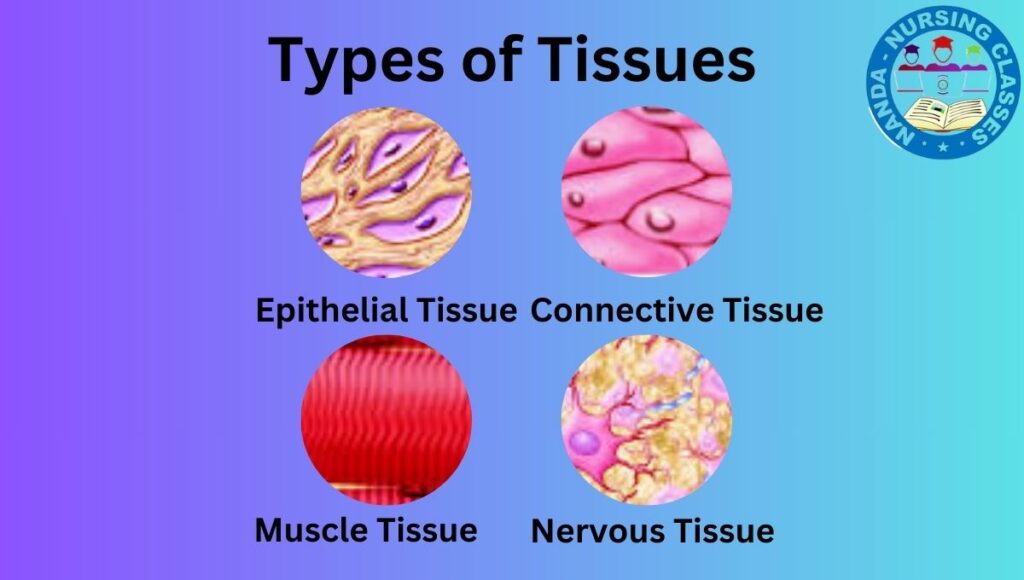
learn all about The Tissue of the human body. In the Second Part,
Summary
The study of human body cavities and organ systems is a fascinating yet challenging journey for nursing students. These well-organized cavities, like the protective dorsal cavity and the functional ventral cavity, offer invaluable insights into the body’s intricate structure. Understanding how organs like the brain, heart, and lungs are safeguarded while performing their essential tasks highlights the remarkable precision of human anatomy. However, the sheer volume of information and the complexity of interconnections between systems can feel overwhelming at times. Despite these hurdles, gaining mastery of this topic is not only rewarding but also crucial for developing the skills and confidence needed to provide exceptional patient care.