Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Procedure
What dose CPR stand for?
The full form of CPR is cardiopulmonary resuscitation . Which means to smooth the functioning of the patient’s heart and breathing. CPR is an emergency situation to save a human being in which the patient’s circulatory system and respiratory system are stopped. Again, it is run smoothly and can be prevented from going into arrest. CPR is usually given when the heart’s normal rhythm is disrupted, preventing it from effectively pumping blood to vital organs.
CPR definition in nursing
CPR is an essential skill that anyone can learn and is often taught in first aid and basic life aid courses. Prompt initiation of CPR can significantly increase the chances of survival until advanced medical assistance arrives.
CPR OBJECTIVE
The objective of giving CPR is mainly to save the life of the patient, the purpose of CPR procedure is to normalize the heart rate of the patient so that oxygen can be provided to the patient’s brain, heart and other vital organs so that it can function smoothly.If the emergency situation does not occur in the hospital, then the objectives of giving CPR in such a situation will be as follows:
- Maintain blood flow to the brain and other vital organs until advanced medical care arrives.
- Give the victim a chance to survive.
- Reduce the risk of brain damage.
CPR PURPOSE
- Maintain blood flow to the brain and other vital organs to restore partial flow of oxygen-rich blood to the brain and heart. Prevent brain damage
- increases chances of survival
- Closes the gap in advanced medical care
- Empowering bystanders (nursing students, students, and others) to perform CPR
In short, CPR plays an important role in the emergency management of cardiac arrest. By maintaining blood flow to vital organs, delaying brain damage, increasing the chances of survival, bridging the gap in advanced care, and empowering bystanders to act, CPR plays a vital role in saving lives.
Indications for giving CPR (CPR INDICATION)
When a person’s respiratory system stops, it can happen due to many reasons such as
-
- You may need to provide CPR after a person has drowned,You may also need to give the patient CPR due to airway obstruction,Any person can cause smoke to enter his respiratory system.You may need to give CPR due to Suffocation or airway obstruction due to any causeYou may need to provide CPR if there is a blockage, or Cardiac arrest: In such a situation you need to give CPR to the patient.
CPR CONTRAINDICATION
- You have to keep in mind that if a patient is moving towards death due to some chronic disease, then CPR should not be given to such a patient.
- Patients who have 0% chance of survival and require hospital care, such diseases are respectively metastatic cancer, renal failure, pneumonia, sepsis, multiple organ failure, acute stroke, or
- CPR should not be given in these circumstances to those who have already been given CPR for 30 minutes.
CPR ARTICLE
- Ambu bag to keep the patient’s respiratory system functioning smoothly.
- Arrest bored (CPR bored) can be placed below the chest of the victim or the patient can also be made to lie down on a flat surface.
- If the patient is in the hospital, oral airway can be used.
CPR steps
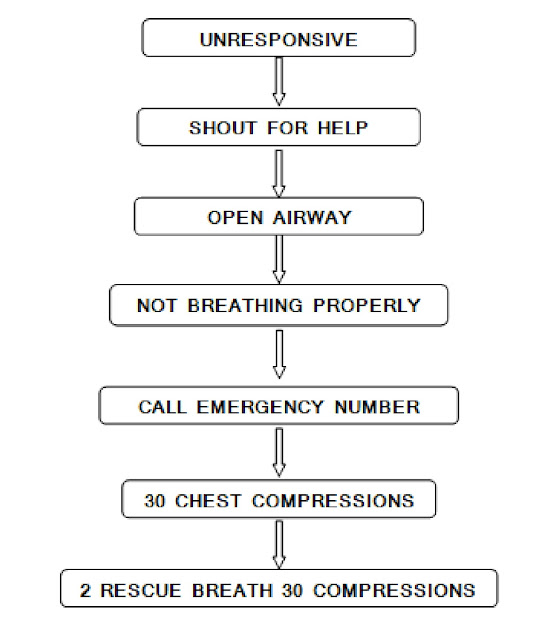
The basic principle of steps to give CPR is based on the lines of ABCDs which are addressed by A=Airway, B=Breathing, C=Circulation and D=Defibrillation respectively.
CPR sequence
Airways
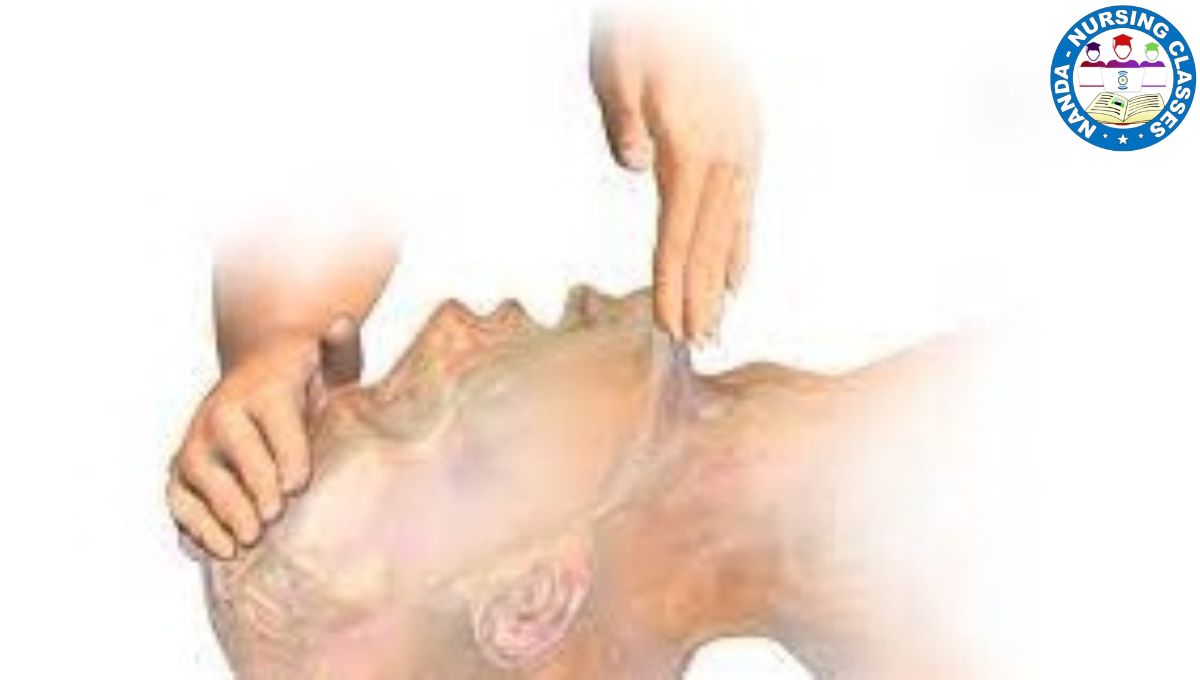
The first stage of CPR is to make the patient’s breathing path (airway) easy and smooth. If there is any item causing obstruction in the patient’s mouth, then it has to be removed. Now you have to straighten the patient’s head to open the airway. For this, you will have to press the patient’s head with one hand and lift the patient’s chin with the other hand so that the patient’s airway can be opened so that the path of breathing gets opened or cleared.
breathing
After the airway is clear, you will have to understand the breathing activity of the patient. Whether the patient is breathing or not. If he is not able to breathe, then to give ventilation to the patient, you will have to give artificial breathing, you can do this using oxygen mask or Will do it with the help of embu beg.

Circulation
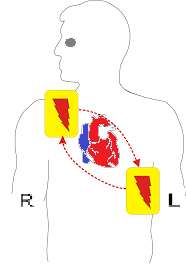
After airway and breathing, you have to start the patient’s blood circulation to keep the heart rate of the patient’s body running smoothly. To start the circulation, you have to give external pressure on the patient’s heart, as a result of which the blood flow gets facilitated so that the circulation can start again. To start the circulation, after giving the right position to the patient, you smoothen the airway and breathing. Hey, now you will come to the side of the patient and place the palm of one hand on his chest in the middle of the sternum bone, then place the other hand on top of the first hand (shown in the picture). You will have to take care that now your fingers are on the chest of the patient. Now you have to apply pressure of about 2 inches and the speed of pressure should be 100 pressures per minute. Now you have to keep in mind that after every 30 compressions, you will have to give artificial breathing twice and you have to do this sequence smoothly.
Defibrillation
Defibrillation is done in CPR procedure when the patient is placed on a cardiac monitor and ventricular fibrillation is detected. With the help of a defibrillator machine, current is applied to the patient so that electric waves can start in the patient’s heart, which can start the heartbeat. CPR should be restarted after possibly 3 shocks.
CPR ALGORITHM
ALGORITHM OF CPR
MEDICATION USED IN CPR
- Oxygen improves oxygenation in the patient’s tissue and cures hypoxemia.
- Epinephrine increases systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure and improves coronary and cerebral perfusion and myocardial contractility.
- Vasopressin also increases systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure.
- Atropine inhibits parasympathetic actions and increases SA node automaticity and AV conduction.
- Sodium bicarbonate (NAHCO3)- improves the amount of acidosis.
- Magnesium improves the efficiency of the cellular sodium-potassium pump.
WHEN WILL YOU STOP CPR
- When the patient’s spontaneous circulation becomes smooth,
- When the EMS team arrives,
- If the person giving CPR gets tired,
And - When the death of the patient is certain
WHY CPR MAY FAIL?
CAUSES FOR THE FAILURE OF CPR
- Having a myocardial infarction
- Cardiac infarction (due to accumulation of fluid around the heart)
- due to obstructed airway
- due to severely diseased or damaged lungs
- Due to pulmonary artery block (Pulmonary embolism)
- causes of chest deformities
- due to chest fracture
- There is a possibility of failure due to not doing the CPR technique properly.
COMPLICATIONS OF CPR
Vomiting and aspiration of fluid
The most serious possibility for the patient during CPR is the possibility of vomiting, which can threaten the patient’s life. Since the patient is unconscious, he or she is unable to clear the vomit from his or her mouth and if the fluid is not cleared, there is a possibility of the fluid blocking his or her lungs and airways while the patient is breathing.
Body Fluid Exposure
While giving CPR, the rescuer is at risk of coming in contact with the patient’s body fluids. The rescuer providing direct mouth-to-mouth rescue to the victim without a mask results in contact of saliva between the victim and the rescuer. Blood and vomit may also be present during CPR, which carries the risk of communicable disease such as hepatitis and AIDS. The American Heart Association encourages the use of a barrier mask while the rescuer is administering breathing to ensure the rescuer’s safety while attempting to save the patient’s life.
Broken Bones
There is a possibility of ribs breaking if the chest is compressed with excessive force. The problem of broken ribs is more common in the elderly due to the brittleness and weakness of their bones. Broken ribs present a danger because a broken rib can potentially puncture (cut) the lung, spleen or liver which are very painful conditions.
Internal Injuries
Chest compression puts pressure on internal organ areas, which can result in broken ribs and chest bones and puncture of the lungs and liver. Additionally, the heart and liver may also suffer internal injury.
Gastric Distention
During CPR the rescuer supplies air directly into the patient’s lungs. If air is given to the patient too often or for too long, air may accumulate in the patient’s stomach, which is called gastric distension. Gastric disturbances cause the stomach to swell and put pressure on the lungs. Complicated CPR efforts may reduce the ability to deliver adequate oxygen to the patient’s lungs. Gastric distention can be avoided if the rescuer provides proper, careful breathing during CPR.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) procedure is paramount for everyone, as it can potentially save lives in emergency situations. By promptly administering CPR, individuals can effectively sustain vital functions until professional medical help arrives. This life-saving technique involves a combination of chest compressions and rescue breaths, which work to maintain circulation and oxygenation to the brain and other vital organs. With proper training and regular practice, anyone can become proficient in performing CPR, contributing to a safer and more resilient community. Remember, being prepared and confident in CPR can make all the difference in a life-or-death scenario.
CPR Procedure in Hindi
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) about CPR:
Who can perform CPR?
CPR can be performed by anyone, regardless of age or background, after receiving proper training. It’s important to remember that even basic CPR knowledge can significantly increase the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest.
What is the correct technique for performing CPR?
The basic steps for CPR include checking for responsiveness, calling for help, performing chest compressions, and delivering rescue breaths. Proper training is essential to ensure the correct technique and maximize effectiveness.
How long should CPR be performed?
CPR should be continued until professional medical help arrives or until the person shows signs of responsiveness. It’s crucial to maintain uninterrupted chest compressions and rescue breaths to sustain circulation and oxygenation.
Can I perform CPR on a child or infant?
Yes, CPR techniques vary slightly for children and infants compared to adults. It’s important to receive specialized training in pediatric CPR to effectively respond to emergencies involving younger individuals.
What if I’m unsure about performing CPR?
If you’re unsure about performing CPR, it’s still crucial to call emergency services immediately. Dispatchers can provide guidance over the phone, and many communities offer CPR training courses to increase confidence and preparedness.
Can CPR cause harm?
A: While CPR may cause some injuries, such as broken ribs or bruising, the benefits of performing CPR far outweigh the risks, especially in life-threatening situations. Proper technique and training can minimize the likelihood of complications.
Is CPR effective?
Yes, CPR can be highly effective in restoring circulation and oxygenation to the body, particularly when administered promptly and correctly. Studies have shown that immediate bystander CPR can double or even triple the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest.