Introduction of Ear Care Procedure in Nursing
Ear Care Procedure in Nursing is performed by the skilled nursing officer of the hospital. The ear care or we can say ear irrigation in other words. Ear irrigation is the washing of the external auditory canal of the ear with a solution prescribed by the doctor. It is a professional ear-cleaning process.
Table of Contents
Ear Care Definition
Ear irrigation is a systematic ear canal washing procedure in which a nurse washes a patient’s ear external canal with liquid solutions. Ear irrigation is usually done to clear the ear canal, clean any discharge, soften and remove ear wax, or remove a foreign body from the patient’s ear.
Ear Care Purposes
- To clean the auditory canal
- To apply heat or cold to the ear
- To remove any foreign object
- To relieve pain
Solutions used in ear irrigation
To care for the ear there are some solutions used only prescribed by the physician of the patient. Some common
solutions used in-ear care are given below:
- Boric acid 2-4%
- Sodium bicarbonate 1%
- Normal saline
- Hydrogen peroxide 2%
- Plain warm water
Indications and Contraindications for Ear Irrigation:
Indications
- Removal of excessive earwax (cerumen) buildup causing hearing impairment or discomfort.
- Preparation of the ear canal for examination or treatment.
- Facilitation of ear medication administration.
Contraindications
- Presence of a perforated eardrum or a history of recurrent perforations.
- Recent ear surgery or injury.
- Suspected or known ear canal obstruction due to foreign objects, tumors, or bony abnormalities.
- Active ear infection or inflammation (otitis externa).
- Severe pain or discomfort during examination, suggesting potential complications.
- Known allergy or sensitivity to irrigation solutions used in the procedure.
- Patient inability to cooperate or follow instructions, particularly in pediatric or cognitively impaired individuals.
General Instructions to be kept in mind whenever performing Ear Care Procedures in Nursing
- Explain the procedure to reduce the patient’s anxiety and gain his cooperation
- The temperature of the irrigating solution should be between 37⁰c and 38⁰c
- Irrigate with the minimum amount of pressure
- The height of the can should be 6inches or 15cm above the level of the ear
- Straighten the external auditory canal by holding pinna of the ear upward and backwards in case of adults, in children pull it downward and backwards
- Expel air from the syringe and tubing before starting the procedure
- Direct the steam of solution towards the wall of the ear canal not towards the tympanic membrane
- If vertigo occurs, stop the procedure immediately
- Ear irrigation should not be done when any grain has gone into the ear, as it may swell up and impact the ear canal
- Carry out the procedure in good light.
Ear Care Procedure Articles Required in Nursing
| S.No. | Articles Used in Ear Care Procedure | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Irrigating solution in a sterile container | To irrigate the ear |
| 2 | IV set | To perform the procedure |
| 3 | Sterile cotton balls and cotton-tipped applicators | To clean the external auditory meatus |
| 4 | Small towel | To protect the patient’s garments |
| 5 | Mackintosh and towel | To protect the bed linen |
| 6 | Kidney tray and paper bag | To collect the waste |
| 7 | Thump forceps | To clean the ear |
| 8 | IV stand | To hang the irrigation solution |
| 9 | Ear medication | To instill into the ear after the irrigation |
A clean tray containing with following articles:
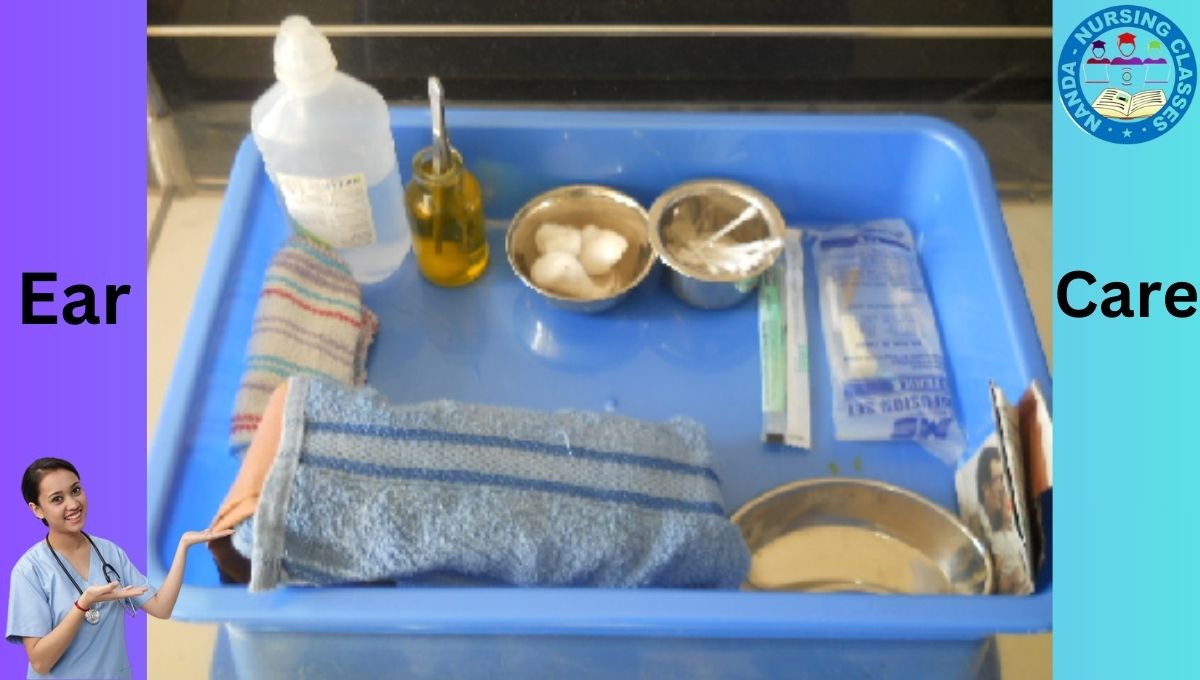
Ear Care Procedure in Nursing
Ear care nursing procedure is performed in the following steps are given below:
| Steps | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Explain the procedure and place the patient in a sitting position or dorsal recumbent position with his head titled towards the affected area | To relieve the patient’s anxiety and gain his cooperation |
| Spread the mackintosh and towel and put the kidney tray close to the head and under the ear | Prevent soiling the bed |
| Sterile cotton balls and cotton-tipped applicators | To clean the external auditory meatus |
| Wash hands | To prevent the transfer of microorganisms |
| Use a cloth swab stick to remove any discharge | To prevent carrying discharge deeper into the canal |
| Test temperature of the solution by pouring at the back of the nurse’s hand and pinna of ear | Extreme temperature causes vertigo |
| Pull the ear gently to straighten the external auditory canal and direct the stream of fluid towards the lateral walls of the auditory canal |
Allows fluid to reach up to the tympanic membrane |
| Observe for signs of pain and vertigo |
To observe the patents abnormality |
| Irrigate the ear till the desired effect is achieved by a steady and continuous flow of the solution |
To achieve the desired result |
| Dry pinna of the ear by using a small towel |
To feel comfortable |
After professional ear cleaning what to do?
- Remove soiled articles and make the patient comfortable.
- Instruct him to lie on the irrigated side for a few minutes after the procedure
- Record the time of irrigation, kind and amount of the solution, nature of the return flow and the effect of the treatment
Tips for preventing ear infections through good ear hygiene practices
- Avoid Inserting Objects: Refrain from inserting cotton swabs, fingers, or any other objects into the ear canal. This can push wax deeper into the ear or even cause injury to the delicate ear structures, increasing the risk of infection.
- Keep Ears Dry: Moisture in the ear canal can create a favorable environment for bacteria and fungi to thrive, leading to infections. After swimming or showering, gently dry your ears with a towel and tilt your head to allow any excess water to drain out.
- Practice Ear Protection: Wear earplugs or a swim cap when swimming to prevent water from entering the ears. In environments with loud noises, such as concerts or construction sites, use earplugs or earmuffs to protect your ears from noise-induced damage, which can predispose you to infections.
- Maintain Cleanliness: Regularly clean the outer ear with a washcloth during your bath or shower. Avoid using harsh soaps or vigorous scrubbing, as this can irritate the skin and disrupt the natural balance of the ear.
- Limit Earphone Usage: If you use earphones or headphones, keep the volume at a moderate level to prevent damage to your hearing. Sharing earphones can also increase the risk of transferring bacteria or fungi, so it’s best to avoid sharing them with others.
- Seek Prompt Treatment: If you experience symptoms such as ear pain, itching, discharge, or hearing loss, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment of ear infections can prevent complications and promote faster recovery.
- Follow Medical Advice: If you have a history of recurrent ear infections or underlying conditions such as allergies or eczema that affect your ears, follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for preventive care, including medication or specialized ear care routines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ear care is a crucial aspect of nursing practice aimed at maintaining the health and well-being of patients. Through proper ear care procedures, nurses can prevent infections, alleviate discomfort, and promote optimal hearing function. By adhering to best practices, including regular assessment, gentle cleaning techniques, and patient education, nurses play a vital role in ensuring the overall ear health of individuals across the lifespan. Continual education and staying updated on evidence-based practices are essential for nurses to provide safe and effective ear care interventions. By prioritizing ear care within nursing practice, healthcare professionals contribute to enhancing the quality of life for their patients.
You must read: Lumbar Puncture Procedure: A Comprehensive Guide
FAQs
What is ear care in nursing?
Ear care in nursing refers to the practices and procedures implemented by healthcare professionals to maintain the cleanliness, health, and function of the ears. It involves assessment, cleaning, and prevention of ear-related issues such as infections and wax buildup.
Why is ear care important in nursing?
Ear care is important in nursing as it helps prevent ear infections, discomfort, and hearing loss. Proper ear care also promotes patient comfort and overall well-being, contributing to better quality of life.
What are some common ear care procedures performed by nurses?
Common ear care procedures performed by nurses include visual inspection of the ears, removal of earwax using appropriate techniques, administration of ear drops for medication or cleaning purposes, and providing patient education on ear hygiene.
How often should ear care be performed?
The frequency of ear care depends on individual patient needs and circumstances. For routine ear hygiene, gentle cleaning with a washcloth during daily bathing is usually sufficient. However, individuals with specific ear conditions or risk factors may require more frequent assessment and care as advised by a healthcare professional.
Can nurses perform ear irrigation?
Ear irrigation, or ear flushing, is a procedure commonly performed by healthcare professionals, including nurses, to remove excessive earwax or foreign objects from the ear canal. Proper training and adherence to established protocols are essential for safe and effective ear irrigation.
What should I do if I experience ear pain or hearing loss?
If you experience ear pain or hearing loss, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional, such as a nurse or doctor, can assess your condition, provide appropriate treatment, and offer guidance on ear care and management.
How can I prevent ear infections?
To prevent ear infections, maintain good ear hygiene by avoiding the use of cotton swabs or other objects to clean the ears, protecting the ears from excessive moisture, and seeking prompt treatment for any ear-related symptoms or issues.
If you have any queries Feel free to ask any Queries in the comment section 👇and share them with your peer groups



